Why are spacing, edge distance, and embedment important for concrete anchors?
Anchors transfer loads into concrete, making them vital for safe design.
Their strength depends not only on the anchor itself but on how it interacts with the concrete.
Three factors are key: spacing, edge distance, and embedment depth. If these are not respected, the anchor may lose capacity and the concrete can crack, spall, or fail.
Understanding these details is essential for designing safe, durable, and code-compliant connections.

Spacing Between Anchors
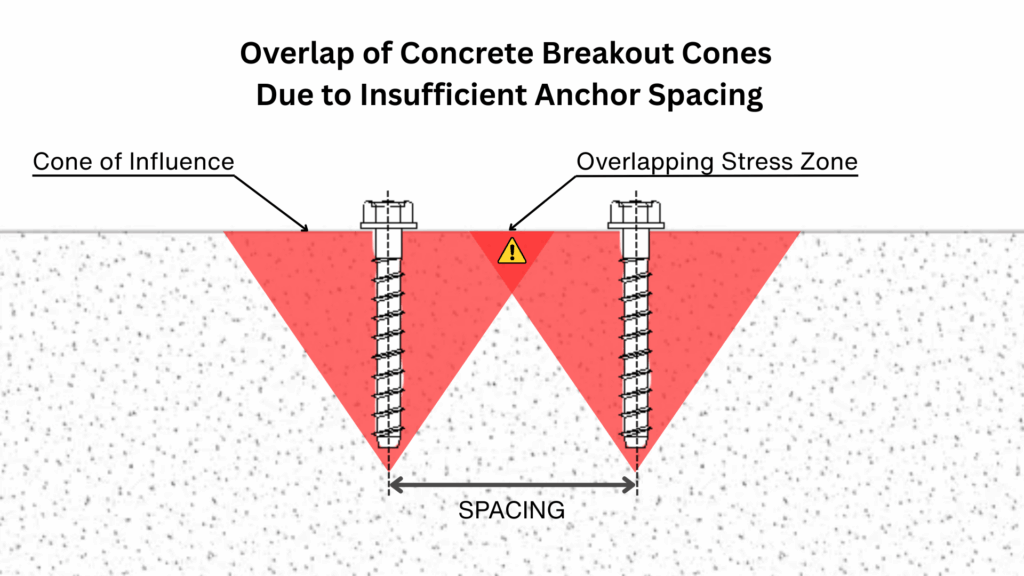
Proper spacing between anchors is essential because concrete doesn’t behave like steel: it is strong in compression but weak in tension. When an anchor is loaded, it spreads stress into the concrete in the shape of a cone. If anchors are too close together, these cones overlap, which means the stresses combine and the concrete between them is forced to carry more tension than it can handle. This often results in splitting or premature cracking, and both anchors lose much of their capacity.
By providing adequate spacing, each anchor can develop its full pullout and shear strength, and the slab or foundation is able to distribute loads safely into the surrounding mass of concrete. This not only increases the reliability of the connection, but also prevents progressive failures, where the failure of one anchor weakens nearby ones.
A good rule of thumb is to keep at least 12 times the anchor diameter as spacing to the next anchor or to a concrete edge. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for the exact values to use.
Edge Distance
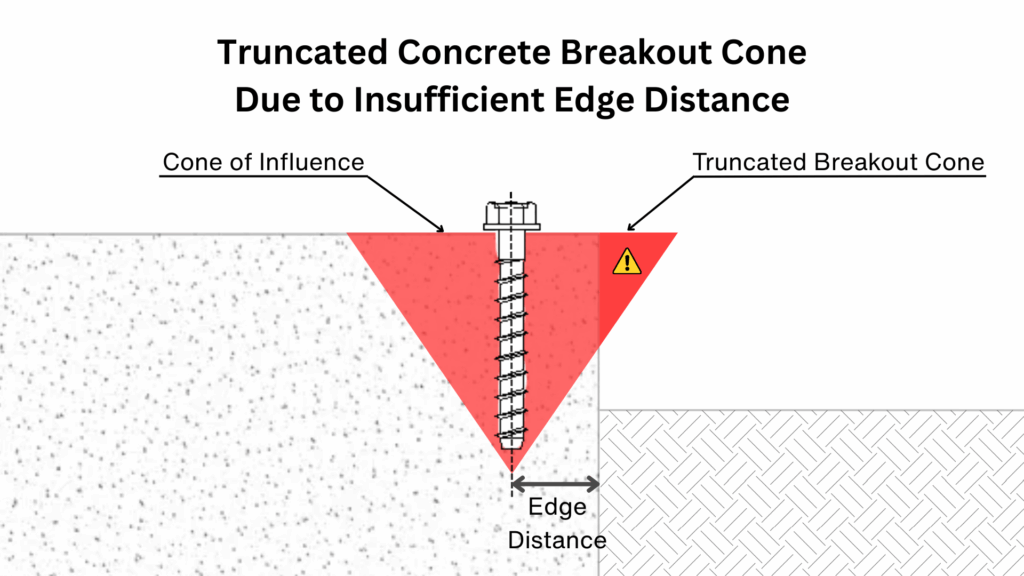
The edge distance is the required spacing between an anchor and the closest free edge of the concrete. It plays a crucial role because the concrete around an anchor transfers the applied loads through a cone-shaped zone of stress.
If the anchor is installed too close to an edge, this cone cannot fully develop within the concrete mass. Instead, the stress zone is cut off, which makes the edge more vulnerable to cracking or spalling. In this situation, the anchor may fail prematurely, not because of the steel itself, but because the surrounding concrete cannot resist the concentrated forces.
Ensuring sufficient edge distance provides the anchor with enough material to distribute loads evenly, improving both the strength of the connection and the durability of the concrete element.
Watch a Demonstration of Edge Breakout !
Embedment Depth
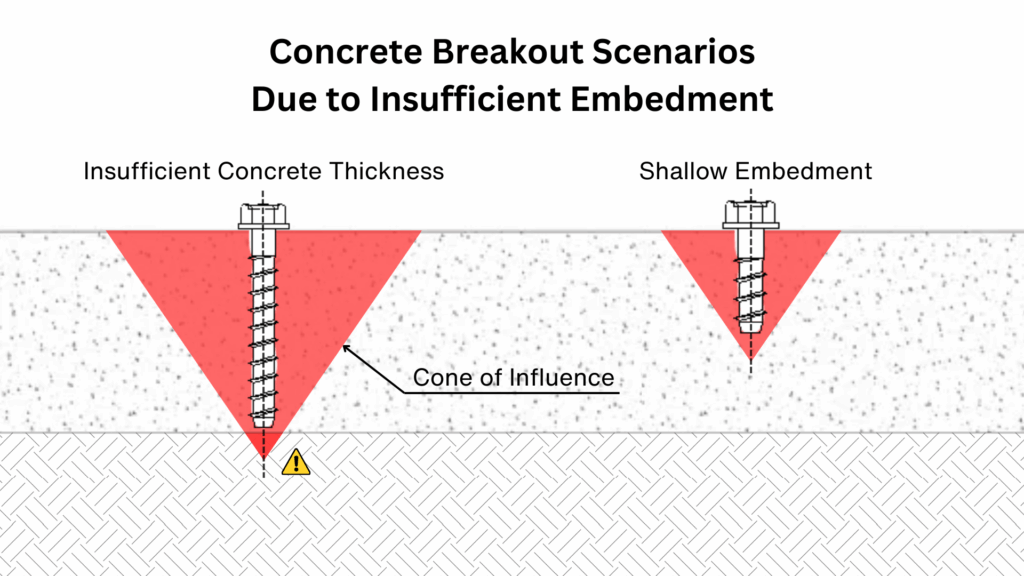
The embedment depth is the distance an anchor is installed into the concrete, and it has a direct impact on its performance. As the anchor’s embedment decreases, the cone of influence becomes smaller, which reduces the amount of concrete engaged. This results in a noticeable decrease in both tensile and shear capacities compared to the maximum tested values.
To ensure proper performance, the concrete thickness must also be considered. A general guideline is that the slab or member should have a thickness of at least 1.5 times the anchor embedment depth. This prevents the breakout cone from extending beyond the bottom surface of the concrete and ensures that the anchor can fully develop its strength.
Providing sufficient embedment depth therefore allows the anchor to transfer forces into a larger volume of concrete, increasing both load resistance and long-term reliability of the connection.
Further Guidance
For safe and reliable design, it is important to go beyond general rules of thumb. Always consult the technical manuals provided by the manufacturer of the anchors you are using, or rely on specialized software that performs these calculations accurately. Most importantly, always consult a qualified design professional before installing any anchors that could affect the life and safety of the public or property.
Here are a few helpful resources:
• DeWalt Anchor Software – Technical Manual
• Hilti PROFIS Engineering – Technical Guides
• Simpson Strong – Technical Guides
For more detailed information and professional support on your future projects, don’t hesitate to contact us. If you have any questions or want to learn more about our services, simply get in touch—click the buttons below to get started.
For more detailed information and guidance on handling your future design projects, check out our online design calculators, contact us for site-specific projects, or reach out to us with your inquiries.
Last Update: November 23, 2025
Related Knowledge Base Posts -
- ASCE 7 WIND EXPOSURE CATEGORIES AND HOW EXPOSURE ‘D’ WORKS
- What is a window or door buck
- What wind information is required for construction documents?
- Understanding Canopies: Design and Load Considerations
- Metal Fasteners UNC vs Spaced Thread
- Minimum Edge Distance Requirements for Bolts & Screws in Metal (Steel & Aluminum)